421 lines
13 KiB
Markdown
421 lines
13 KiB
Markdown
# tabtab
|
|
|
|
[](https://travis-ci.org/mklabs/tabtab)
|
|
[](https://coveralls.io/github/mklabs/tabtab?branch=3.0.0)
|
|
|
|
A node package to do some custom command line `<tab><tab>` completion for any
|
|
system command, for Bash, Zsh, and Fish shells.
|
|
|
|
Made possible using the same technique as npm (whose completion is quite
|
|
awesome) relying on a shell script bridge to do the actual completion from
|
|
node's land.
|
|
|
|
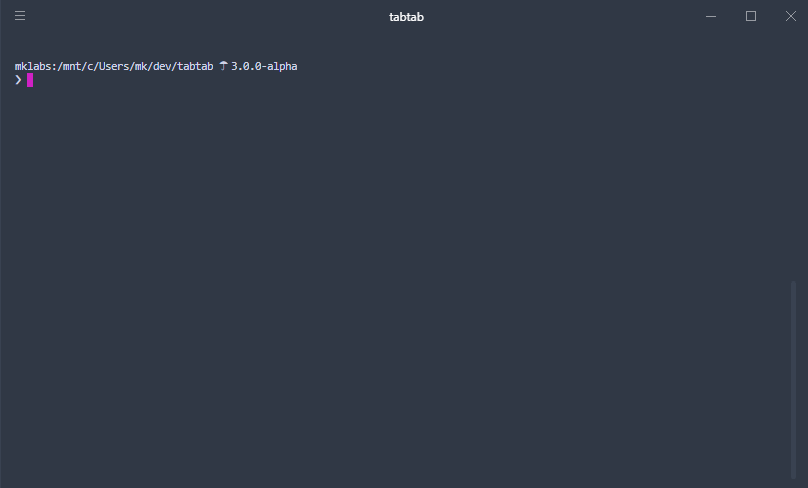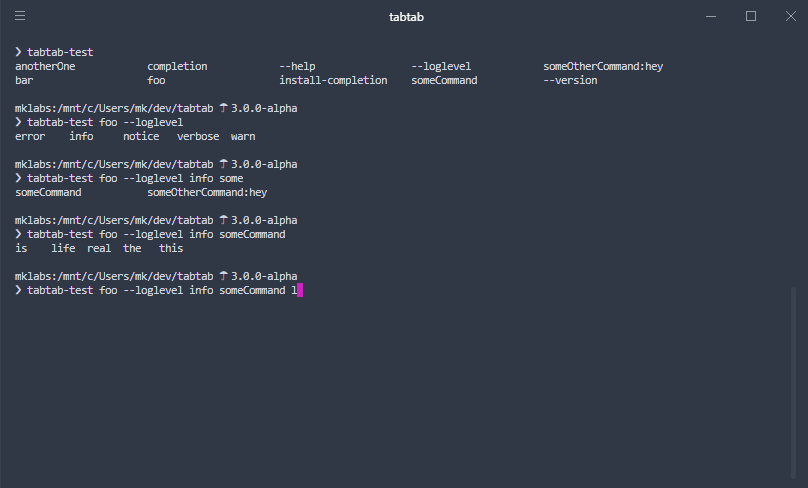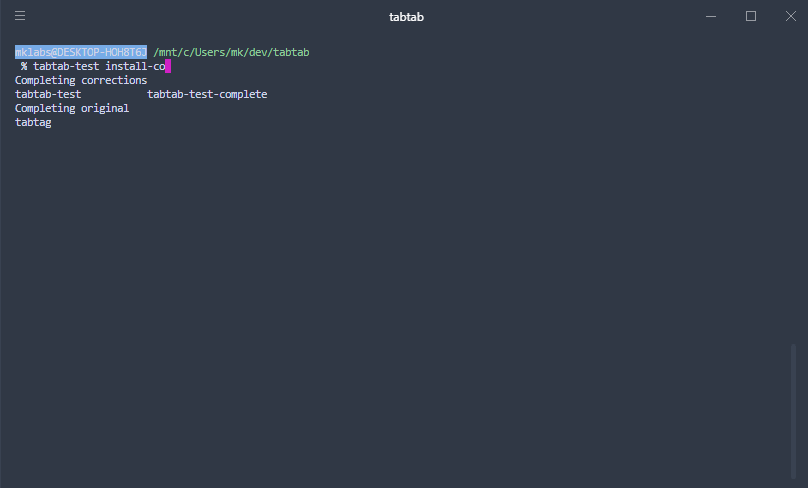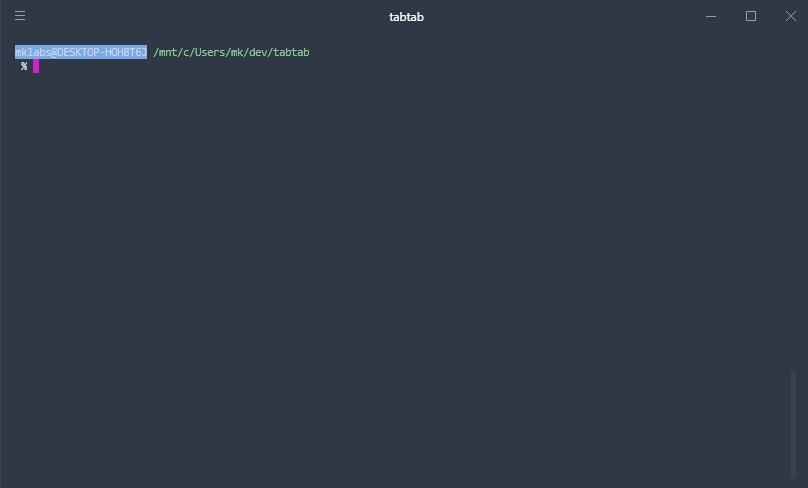
|
|
|
|
**Warning / Breaking changes**
|
|
|
|
- Windows is not supported
|
|
- Cache has been removed
|
|
- Now only support node `> 7.10.1`, for previous version with support for node
|
|
6 be sure to use tabtab `2.2.x`
|
|
|
|
## Table of Contents
|
|
|
|
- [Goal of this 3.0.0 version](#goal-of-this-300-version)
|
|
|
|
- [Installation](#installation)
|
|
|
|
- [Usage](#usage)
|
|
|
|
- [1. Install completion](#1-install-completion)
|
|
- [2. Log completion](#2-log-completion)
|
|
- [3. Parsing env](#3-parsing-env)
|
|
|
|
- [Completion mechanism](#completion-mechanism)
|
|
|
|
- [Completion install](#completion-install)
|
|
- [Completion uninstall](#completion-uninstall)
|
|
|
|
- [Debugging](#debugging)
|
|
|
|
- [API Documentation](#api-documentation)
|
|
|
|
- [Changelog](#changelog)
|
|
|
|
- [Credits](#credits)
|
|
|
|
## Goal of this 3.0.0 version
|
|
|
|
Simplify everything, major overhaul, rewrite from scratch.
|
|
|
|
Functional, less abstraction, clearer documentation, good test coverage,
|
|
support for node 10 without babel.
|
|
|
|
Up to date dependencies, easier to debug, easier to test.
|
|
|
|
Should still support bash, zsh and fish but bash is the primary focus of this
|
|
alpha version.
|
|
|
|
No binary file anymore, just a library (still debating with myself)
|
|
|
|
The goal of this rewrite is two-folded:
|
|
|
|
- Integrate nicely with [yo](https://github.com/yeoman/yo) (Yeoman)
|
|
- Have a robust and fast enough library for [yarn-completions](https://github.com/mklabs/yarn-completions)
|
|
|
|
## Installation
|
|
|
|
npm install tabtab
|
|
|
|
## Usage
|
|
|
|
Writing completion is a two-step process: Installation and Logging. Tabtab
|
|
provides just that.
|
|
|
|
Here is a basic example using
|
|
[minimist](https://www.npmjs.com/package/minimist) to parse arguments.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
#! /usr/bin/env node
|
|
|
|
const tabtab = require('tabtab');
|
|
const opts = require('minimist')(process.argv.slice(2), {
|
|
string: ['foo', 'bar'],
|
|
boolean: ['help', 'version', 'loglevel']
|
|
});
|
|
|
|
const args = opts._;
|
|
const completion = env => {
|
|
if (!env.complete) return;
|
|
|
|
// Write your completions there
|
|
|
|
if (env.prev === 'foo') {
|
|
return tabtab.log(['is', 'this', 'the', 'real', 'life']);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if (env.prev === 'bar') {
|
|
return tabtab.log(['is', 'this', 'just', 'fantasy']);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if (env.prev === '--loglevel') {
|
|
return tabtab.log(['error', 'warn', 'info', 'notice', 'verbose']);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
return tabtab.log([
|
|
'--help',
|
|
'--version',
|
|
'--loglevel',
|
|
'foo',
|
|
'bar',
|
|
'install-completion',
|
|
'completion',
|
|
'someCommand:someCommand is some kind of command with a description',
|
|
{
|
|
name: 'someOtherCommand:hey',
|
|
description: 'You must add a description for items with ":" in them'
|
|
},
|
|
'anotherOne'
|
|
]);
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
const run = async () => {
|
|
const cmd = args[0];
|
|
|
|
// Write your CLI there
|
|
|
|
// Here we install for the program `tabtab-test` (this file), with
|
|
// completer being the same program. Sometimes, you want to complete
|
|
// another program that's where the `completer` option might come handy.
|
|
if (cmd === 'install-completion') {
|
|
await tabtab
|
|
.install({
|
|
name: 'tabtab-test',
|
|
completer: 'tabtab-test'
|
|
})
|
|
.catch(err => console.error('INSTALL ERROR', err));
|
|
|
|
return;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
if (cmd === 'uninstall-completion') {
|
|
// Here we uninstall for the program `tabtab-test` (this file).
|
|
await tabtab
|
|
.uninstall({
|
|
name: 'tabtab-test'
|
|
})
|
|
.catch(err => console.error('UNINSTALL ERROR', err));
|
|
|
|
return;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// The completion command is added automatically by tabtab when the program
|
|
// is completed.
|
|
if (cmd === 'completion') {
|
|
const env = tabtab.parseEnv(process.env);
|
|
return completion(env);
|
|
}
|
|
};
|
|
|
|
run();
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Please refer to the
|
|
[examples/tabtab-test-complete](./examples/tabtab-test-complete) package for a
|
|
working example. The following usage documentation is based on it.
|
|
|
|
### 1. Install completion
|
|
|
|
To enable completion for a given program or package, you must enable the
|
|
completion on your or user's system. This is done by calling `tabtab.install()`
|
|
usually behind a `program install-completion` command or something similar.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
// Here we install for the program `tabtab-test`, with completer being the same
|
|
// program. Sometimes, you want to complete another program that's where the
|
|
// `completer` option might come handy.
|
|
tabtab.install({
|
|
name: 'tabtab-test',
|
|
completer: 'tabtab-test'
|
|
})
|
|
.then(() => console.log('Completion installed'))
|
|
.catch(err => console.error(err))
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The method returns a promise, so `await / async` usage is possible. It takes an
|
|
`options` parameter, with:
|
|
|
|
- `name`: The program to complete
|
|
- `completer`: The program that does the completion (can be the same program).
|
|
|
|
`tabtab.install()` will ask the user which SHELL to use, and optionally a path
|
|
to write to. This will add a new line to either `~/.bashrc`, `~/.zshrc` or
|
|
`~/.config/fish/config.fish` file to source tabtab completion script.
|
|
|
|
Only one line will be added, even if it is called multiple times.
|
|
|
|
### 2. Log completion
|
|
|
|
Once the completion is enabled and active, you can write completions for the
|
|
program (here, in this example `tabtab-test`). Briefly, adding completions is
|
|
as simple as logging output to `stdout`, with a few particularities (namely on
|
|
Bash, and for descriptions), but this is taken care of by `tabtab.log()`.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
tabtab.log([
|
|
'--help',
|
|
'--version',
|
|
'command'
|
|
'command-two'
|
|
]);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
This is the simplest way of adding completions. You can also use an object,
|
|
instead of a simple string, with `{ name, description }` property if you want
|
|
to add descriptions for each completion item, for the shells that support them
|
|
(like Zsh or Fish). Or use the simpler `name:description` form.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
tabtab.log([
|
|
{ name: 'command', description: 'Description for command' },
|
|
'command-two:Description for command-two'
|
|
]);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The `{ name, description }` approach is preferable in case you have completion
|
|
items with `:` in them.
|
|
|
|
Note that you can call `tabtab.log()` multiple times if you prefer to do so, it
|
|
simply logs to the console in sequence.
|
|
|
|
### 3. Parsing env
|
|
|
|
If you ever want to add more intelligent completion, you'll need to check and
|
|
see what is the last or previous word in the completed line, so that you can
|
|
add options for a specific command or flag (such as loglevels for `--loglevel`
|
|
for instance).
|
|
|
|
Tabtab adds a few environment variables for you to inspect and use, this is
|
|
done by calling `tabtab.parseEnv()` method.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
const env = tabtab.parseEnv(process.env);
|
|
// env:
|
|
//
|
|
// - complete A Boolean indicating whether we act in "plumbing mode" or not
|
|
// - words The Number of words in the completed line
|
|
// - point A Number indicating cursor position
|
|
// - line The String input line
|
|
// - partial The String part of line preceding cursor position
|
|
// - last The last String word of the line
|
|
// - lastPartial The last word String of partial
|
|
// - prev The String word preceding last
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Usually, you'll want to check against `env.last` or `env.prev`.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
if (env.prev === '--loglevel') {
|
|
tabtab.log(['error', 'warn', 'info', 'notice', 'verbose']);
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Completion mechanism
|
|
|
|
Feel free to browse the [scripts](./scripts) directory to inspect the various
|
|
template files used when creating a completion with `tabtab.install()`.
|
|
|
|
Here is a Bash completion snippet created by tabtab.
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
###-begin-tabtab-test-completion-###
|
|
if type complete &>/dev/null; then
|
|
_tabtab-test_completion () {
|
|
local words cword
|
|
if type _get_comp_words_by_ref &>/dev/null; then
|
|
_get_comp_words_by_ref -n = -n @ -n : -w words -i cword
|
|
else
|
|
cword="$COMP_CWORD"
|
|
words=("${COMP_WORDS[@]}")
|
|
fi
|
|
|
|
local si="$IFS"
|
|
IFS=$'\n' COMPREPLY=($(COMP_CWORD="$cword" \
|
|
COMP_LINE="$COMP_LINE" \
|
|
COMP_POINT="$COMP_POINT" \
|
|
tabtab-test completion -- "${words[@]}" \
|
|
2>/dev/null)) || return $?
|
|
IFS="$si"
|
|
if type __ltrim_colon_completions &>/dev/null; then
|
|
__ltrim_colon_completions "${words[cword]}"
|
|
fi
|
|
}
|
|
complete -o default -F _tabtab-test_completion tabtab-test
|
|
fi
|
|
###-end-tabtab-test-completion-###
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
The system is quite simple (though hard to nail it down, thank you npm). A new
|
|
Bash function is created, which is invoked whenever `tabtab-test` is tab
|
|
completed. This function then invokes the completer `tabtab-test completion`
|
|
with `COMP_CWORD`, `COMP_LINE` and `COMP_POINT` environment variables (which is
|
|
parsed by `tabtab.parseEnv()`).
|
|
|
|
The same mechanism can be applied to Zsh and Fish.
|
|
|
|
### Completion install
|
|
|
|
As described in the [`Usage > Install Completion`](#1-install-completion)
|
|
section, installing a completion involves adding a new line to source in either
|
|
`~/.bashrc`, `~/.zshrc` or `~/.config/fish/config.fish` file.
|
|
|
|
In the `3.0.0` version, it has been improved to only add a single line instead
|
|
of multiple ones, one for each completion package installed on the system.
|
|
|
|
This way, a single line is added to enable the completion of for various
|
|
programs without cluttering the Shell configuration file.
|
|
|
|
Example for `~/.bashrc`
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
# tabtab source for packages
|
|
# uninstall by removing these lines
|
|
[ -f ~/.config/tabtab/__tabtab.bash ] && . ~/.config/tabtab/__tabtab.bash || true
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
It'll load a file `__tabtab.bash`, created in the `~/.config/tabtab` directory,
|
|
which will hold all the source lines for each tabtab packages defining a
|
|
completion.
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
# tabtab source for foo package
|
|
# uninstall by removing these lines
|
|
[ -f ~/.config/tabtab/foo.bash ] && . ~/.config/tabtab/foo.bash || true
|
|
|
|
# tabtab source for tabtab-test package
|
|
# uninstall by removing these lines
|
|
[ -f ~/.config/tabtab/tabtab-test.bash ] && . ~/.config/tabtab/tabtab-test.bash || true
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Completion uninstall
|
|
|
|
You can follow the file added in your SHELL configuration file and disable a
|
|
completion by removing the above lines.
|
|
|
|
Or simply disable tabtab by removing the line in your SHELL configuration file.
|
|
|
|
Or, you can use `tabtab.uninstall()` to do this for you.
|
|
|
|
```js
|
|
if (cmd === 'uninstall-completion') {
|
|
// Here we uninstall for the program `tabtab-test`
|
|
await tabtab
|
|
.uninstall({
|
|
name: 'tabtab-test'
|
|
})
|
|
.catch(err => console.error('UNINSTALL ERROR', err));
|
|
|
|
return;
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Debugging
|
|
|
|
tabtab internally logs a lot of things, using the
|
|
[debug](https://www.npmjs.com/package/debug) package.
|
|
|
|
When testing a completion, it can be useful to see those logs, but writing to
|
|
`stdout` or `stderr` while completing something can be troublesome.
|
|
|
|
You can use the `TABTAB_DEBUG` environment variable to specify a file to log to
|
|
instead.
|
|
|
|
export TABTAB_DEBUG="/tmp/tabtab.log"
|
|
tail -f /tmp/tabtab.log
|
|
|
|
# in another shell
|
|
tabtab-test <tab>
|
|
|
|
See [tabtabDebug.js](./lib/utils/tabtabDebug.js) file for details.
|
|
|
|
## API Documentation
|
|
|
|
Please refer to [api](./api) directory to see generated documentation (using
|
|
[jsdoc2md](https://github.com/jsdoc2md/jsdoc-to-markdown))
|
|
|
|
## Changelog
|
|
|
|
Please refer to [CHANGELOG](./CHANGELOG.md) file to see all possible changes to this project.
|
|
|
|
## Credits
|
|
|
|
npm does pretty amazing stuff with its completion feature. bash and zsh
|
|
provides command tab-completion, which allow you to complete the names
|
|
of commands in your $path. usually these functions means bash
|
|
scripting, and in the case of npm, it is partially true.
|
|
|
|
there is a special `npm completion` command you may want to look around,
|
|
if not already.
|
|
|
|
npm completion
|
|
|
|
running this should dump [this
|
|
script](https://raw.github.com/isaacs/npm/caafb7323708e113d100e3e8145b949ed7a16c22/lib/utils/completion.sh)
|
|
to the console. this script works with both bash/zsh and map the correct
|
|
completion functions to the npm executable. these functions takes care
|
|
of parsing the `comp_*` variables available when hitting tab to complete
|
|
a command, set them up as environment variables and run the `npm
|
|
completion` command followed by `-- words` where words match value of
|
|
the command being completed.
|
|
|
|
this means that using this technique npm manage to perform bash/zsh
|
|
completion using node and javascript. actually, the comprehensiveness of npm
|
|
completion is quite amazing.
|
|
|
|
this whole package/module is based entirely on npm's code and @isaacs
|
|
work.
|
|
|
|
* * *
|
|
|
|
> [mit](./LICENSE) · > [mklabs.github.io](https://mklabs.github.io) · > [@mklabs](https://github.com/mklabs)
|